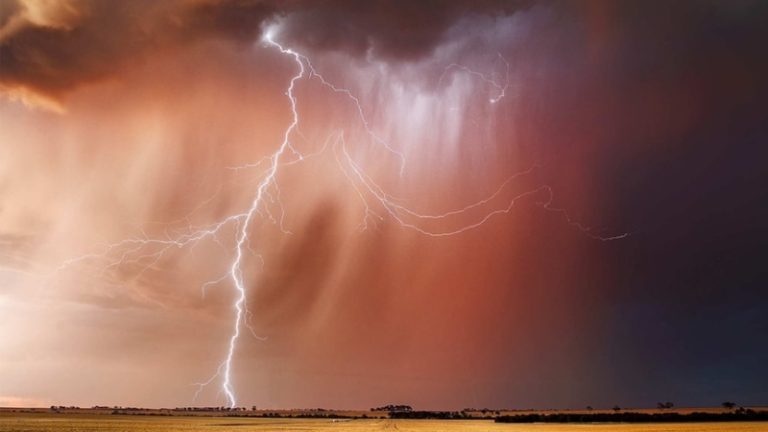
Lightning strikes during a storm in Dowerin in Western Australia's Wheatbelt. (Supplied: Jordan Cantelo)
In short:
Australian researchers have teamed up with NASA to combat devastating bushfires sparked by lightning.
The IGNIS Project will study lightning in a dry-lightning hotspot to provide earlier detection of bushfires.
What's next?
The project will expand to other parts of Australia.
Australian researchers have joined forces with NASA to combat bushfires sparked by lightning across the country.
Lightning sparks hundreds of bushfires each year in Western Australia, according to the Department of Fire and Emergency Services.
It said many were in remote areas that could burn for days before an alert was issued.
This week, a series of dry lightning strikes near Manjimup, about 300 kilometres south of Perth, ignited 14 fires which burned for several days.
WA's South West, a recognised hotspot for bushfires and dry lightning, has been selected as the initial focus point for the IGNIS Project.
The project includes real-time detection and 3D images of lightning at it occurs in a bid to help firefighters with early detection.
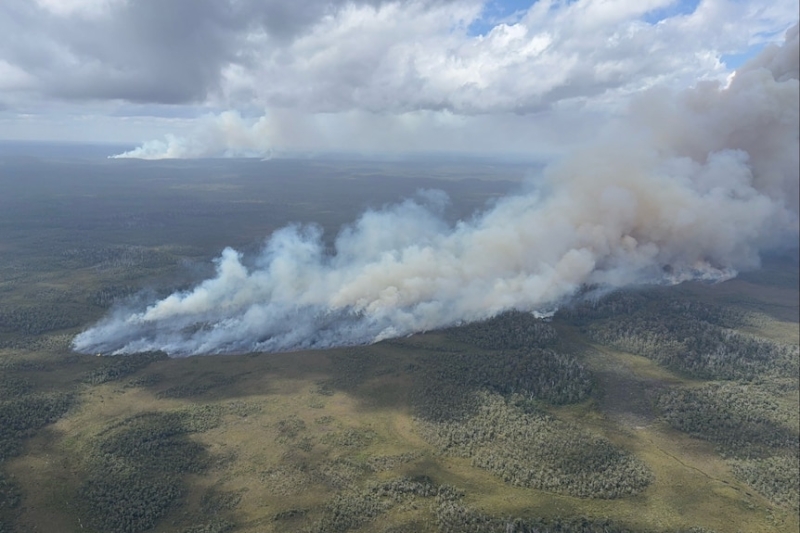

Several bushfires were sparked by dry lighting strikes at the weekend. (Supplied: DFES)
An earlier window
Project lead Paulo de Souza said his team hoped to provide emergency services with earlier notice of lightning-sparked bushfires.
"We hope this information could save properties, could save lives, could save livestock, could preserve our infrastructure," the Edith Cowan University academic said.
"We have our firefighters in the field trying to combat fires when they are already out of control, so we want to give them this edge."
About 100 square kilometres of land south east of Beverley has already been mapped, with 10 stations poised to provide real-time detection and 3D imaging of lightning as it occurs.
Professor de Souza said lightning strikes in remote areas were common but often went undetected for days.
"There is a continuous current lightning … the amount of energy that they discharge, it's huge," he said.
"You have something like a fireplace sleeping there, if you put a little bit of wind on that, that will start firing again.
"So that is the one that we want to collect … we say, 'OK, this is a good candidate for fire'. You can go fly over with cameras that can detect heat."
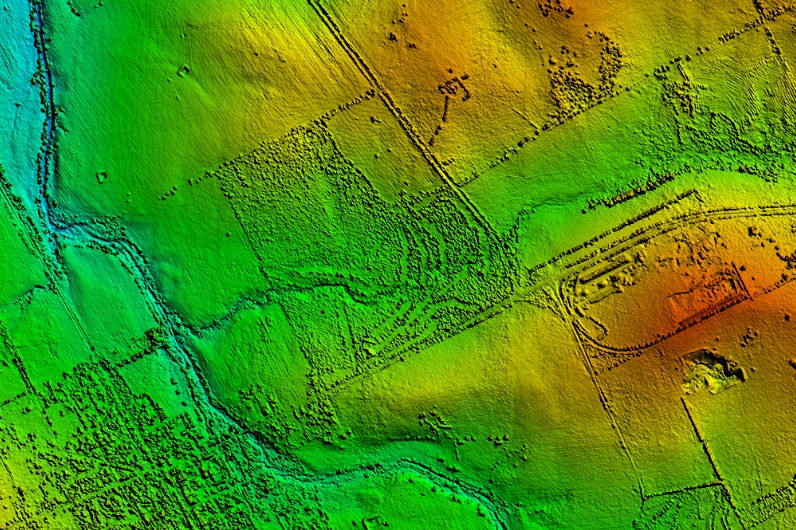
Aerial infrared imaging was completed in the Wheatbelt near Beverley. (Supplied: Edith Cowan University)
The IGNIS Project also has plans to launch a satellite into low earth orbit to track thermal and lightning patterns.
The information will be made available to emergency services to provide an earlier window for intervention, particularly for fires that are ignited by lightning in remote areas.
Professor De Souza said if the technology proved effective, it could be rolled out to fire-prone regions such as South Australia, Victoria, New South Wales and south-east Queensland.
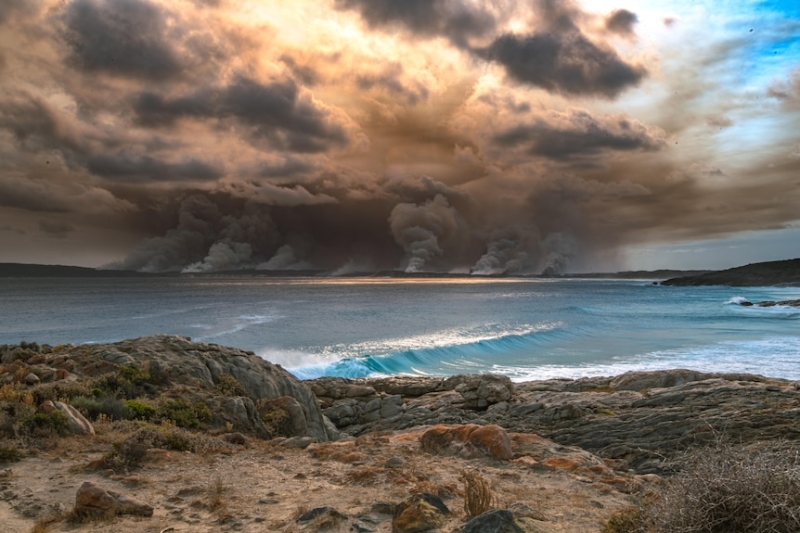

A bushfire was sparked near Bremer Bay during an intense period of lighting in 2022. (Supplied: Jesse Gread)
Dry lightning
While the northern tropical regions of Australia experience more frequent lightning, it is often accompanied by rain.
Bureau of Meteorology community information officer Daniel Hayes said there were two main types of lightning to consider.
"You've got the lightning strikes that are cloud-to-ground, they're the ones that people see the big forks of lightning," Mr Hayes said.
"But you have a lot of lightning that is just within the cloud, cloud-to-cloud type lightning, it never actually strikes the ground, but it is still there and that will be counted by a lot of the measurements."
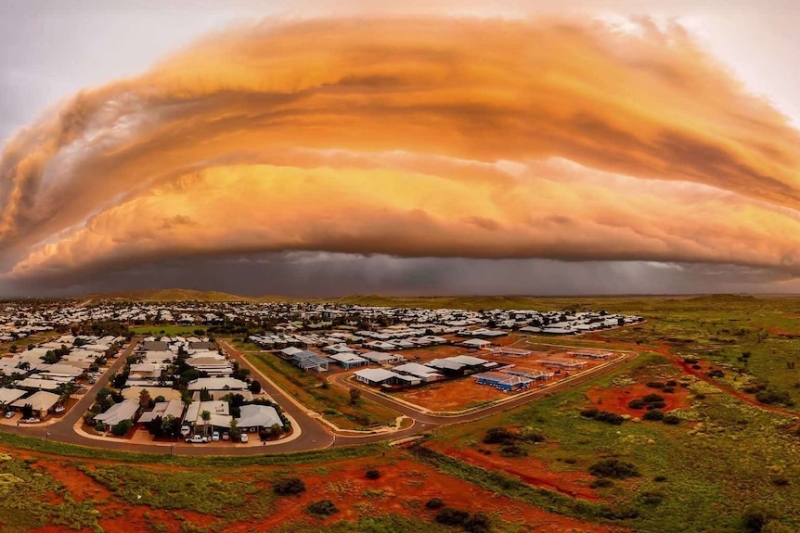

A storm closes in on Karratha in the Pilbara. (Supplied: Simmo Overton)
In terms of fire risk, he said "dry lightning" remained the greater concern.
"When you get those storms come through where you don't necessarily have a whole lot of rain, you can still get those lightning strikes that come through," he said.
"You get basically what's referred to as dry lightning.
"So you get those impacts that can start the fires and there's no rain to actually stop that before it can do any damage."
ABC Great Southern — local news in your inbox
Get our local newsletter, delivered free each ThursdayYour information is being handled in accordance with the ABC Privacy Collection Statement.